Performance Optimization (Profiling & Re-renders) with React DevTools Profiler
Master React performance optimization with React DevTools Profiler. Learn how to analyze re-renders, detect bottlenecks, and apply best practices like memoization and useCallback.
Introduction: Why Performance Matters in React
React apps can sometimes feel slow, even when the code seems fine. The culprit is often unnecessary re-renders. Think of it like refreshing an entire webpage just to update a single button. Optimization makes apps smoother and more efficient.
What Are Re-renders? (Beginner-Friendly Explanation)
A re-render happens when React recalculates a component's output. Imagine redrawing a whole painting just because you changed one small corner. Sometimes it's necessary, but often it's wasted work.
Why Do Extra Re-renders Happen?
- Parent state updates: Even if child props don’t change, children still re-render.
- New object/array references: {} and [] create new memory references every render.
- Anonymous functions in JSX: Each re-render creates a new function.
- Context updates: Context changes cascade across all consumers.
- Skipping memoization: Without useMemo, React recalculates expensive results every time.
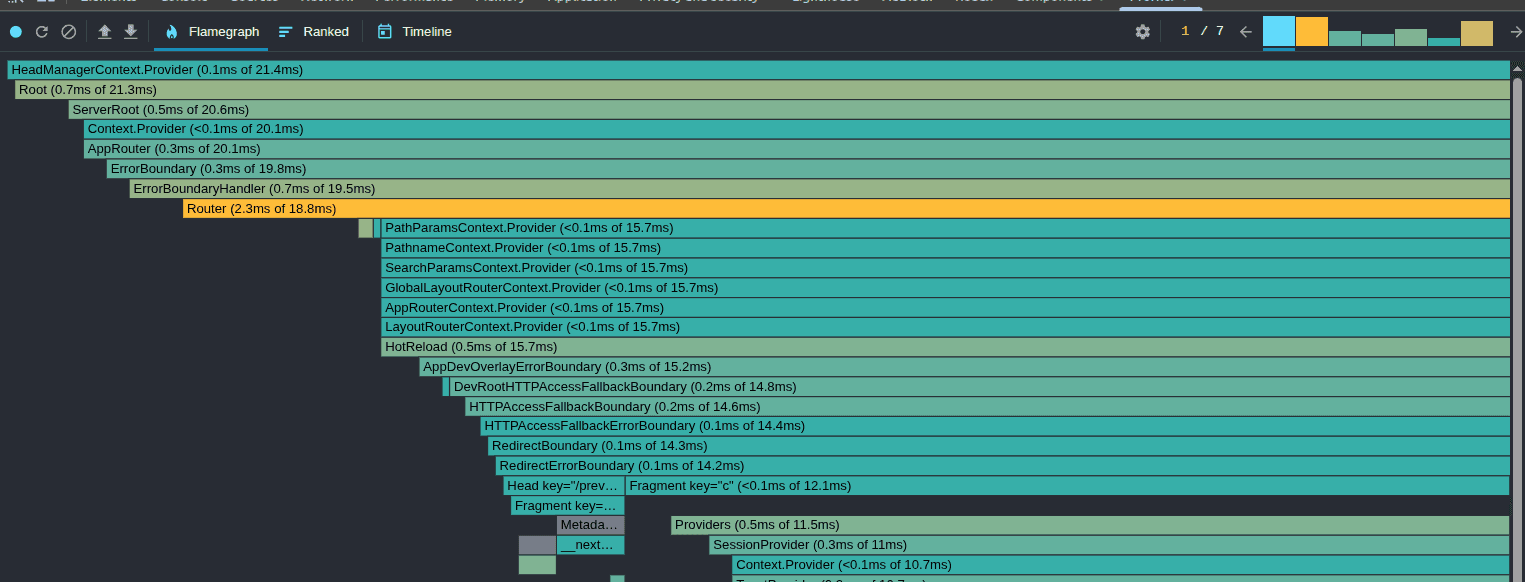
Step-by-Step: Profiling with React DevTools
- Install React DevTools extension in Chrome or Firefox.
- Open your app, go to Profiler tab.
- Click Start Profiling, then use your app as normal.
- Stop profiling to see performance charts.
- Look for components that re-render often or take too long.
Practical Example: Optimizing a List
import React, { useState, useMemo } from 'react';
export default function SearchableList({ items }) {
const [query, setQuery] = useState('');
const filteredItems = useMemo(() => {
console.log('Filtering expensive list...');
return items.filter(item => item.toLowerCase().includes(query.toLowerCase()));
}, [items, query]);
return (
<div>
<input value={query} onChange={e => setQuery(e.target.value)} />
<ul>
{filteredItems.map((item, i) => <li key={i}>{item}</li>)}
</ul>
</div>
);
}Without useMemo, React would re-filter the entire list on every keystroke. With memoization, recalculation only happens when the query or list changes.
Analogy: Memoization Explained Simply
Memoization is like saving a solved puzzle in a box. Next time, you don’t rebuild it piece by piece—you just reuse the completed puzzle. This saves time in React computations.
Do’s and Don’ts of React Optimization
- ✅ Profile your app first before optimizing.
- ✅ Use React.memo for pure presentational components.
- ✅ Use useCallback for event handlers passed as props.
- ❌ Don’t wrap everything in useMemo (adds overhead).
- ❌ Don’t forget dependencies in hook arrays.
Optimization Toolkit Cheat Sheet
| Technique | What It Does | When to Use |
| React.memo | Skips re-render if props haven't changed | Stateless components |
| useMemo | Caches expensive values | Filtering/sorting lists |
| useCallback | Memoizes functions | Stable event handlers |
| Virtualization | Renders only visible items | Large lists/tables |
| Code splitting | Reduces bundle size | Apps with many routes |
Real-World Example: Slow Dashboard
Imagine a dashboard with 20 charts. If one filter changes, all charts re-render, even untouched ones. Using React.memo with stable props ensures only the relevant charts update, making the UI much faster.
FAQs (Beginner Friendly)
- Q: Should I memoize everything? A: No. Only when components render often or expensive calculations exist.
- Q: What’s the difference between useMemo and useCallback? A: useMemo caches a computed value, useCallback caches a function.
- Q: My app is slow, where do I start? A: Use React DevTools Profiler to measure before making changes.
Summary: Key Takeaways
- Measure with Profiler before optimizing.
- Prevent unnecessary renders with memoization.
- Focus optimizations on expensive operations like lists and charts.
- Don’t over-optimize—balance performance with readability.
Conclusion
Performance isn’t about removing all re-renders—it’s about making them efficient. With DevTools Profiler and memoization patterns (React.memo, useMemo, useCallback), React apps can stay smooth, fast, and scalable.